GitLab Kubernetes / OpenShift integration
CAUTION: Warning: The Kubernetes service integration has been deprecated in GitLab 10.3. If the service is active, the cluster information will still be editable, however we advise to disable and reconfigure the clusters using the new Clusters page. If the service is inactive, the fields will not be editable. Read GitLab 10.3 release post for more information.
GitLab can be configured to interact with Kubernetes, or other systems using the Kubernetes API (such as OpenShift).
Each project can be configured to connect to a different Kubernetes cluster, see the configuration section.
Configuration
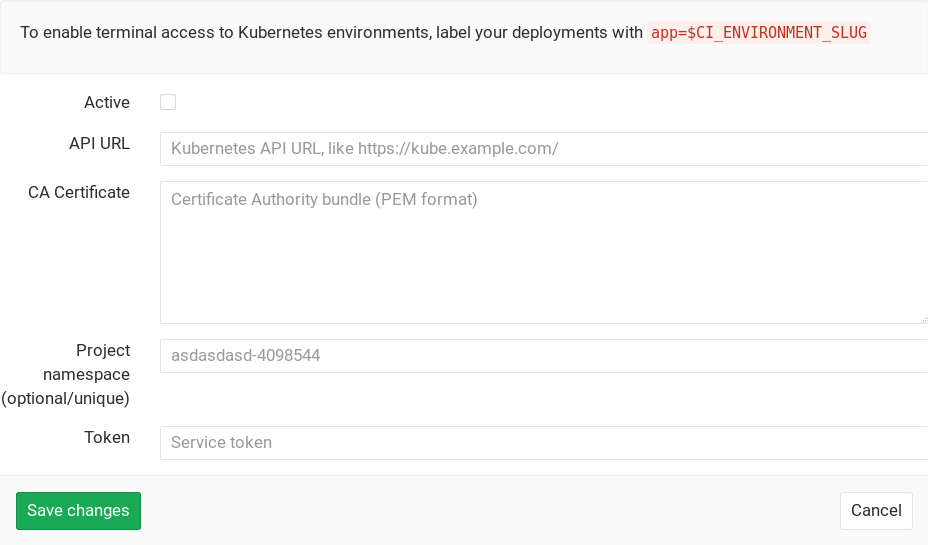
Navigate to the Integrations page of your project and select the Kubernetes service to configure it. Fill in all the needed parameters, check the "Active" checkbox and hit Save changes for the changes to take effect.
The Kubernetes service takes the following parameters:
-
API URL -
It's the URL that GitLab uses to access the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes
exposes several APIs, we want the "base" URL that is common to all of them,
e.g.,
https://kubernetes.example.comrather thanhttps://kubernetes.example.com/api/v1. -
CA certificate (optional) -
If the API is using a self-signed TLS certificate, you'll also need to include
the
ca.crtcontents here. -
Project namespace (optional) - The following apply:
- By default you don't have to fill it in; by leaving it blank, GitLab will create one for you.
- Each project should have a unique namespace.
- The project namespace is not necessarily the namespace of the secret, if
you're using a secret with broader permissions, like the secret from
default. - You should not use
defaultas the project namespace. - If you or someone created a secret specifically for the project, usually with limited permissions, the secret's namespace and project namespace may be the same.
-
Token -
GitLab authenticates against Kubernetes using service tokens, which are
scoped to a particular
namespace. If you don't have a service token yet, you can follow the Kubernetes documentation to create one. You can also view or create service tokens in the Kubernetes dashboard (under Config > Secrets).
TIP: Tip: If you have a single cluster that you want to use for all your projects, you can pre-fill the settings page with a default template. To configure the template, see Services Templates.
Deployment variables
The Kubernetes service exposes the following deployment variables in the GitLab CI/CD build environment:
-
KUBE_URL- Equal to the API URL. -
KUBE_TOKEN- The Kubernetes token. -
KUBE_NAMESPACE- The Kubernetes namespace is auto-generated if not specified. The default value is<project_name>-<project_id>. You can overwrite it to use different one if needed, otherwise theKUBE_NAMESPACEvariable will receive the default value. -
KUBE_CA_PEM_FILE- Only present if a custom CA bundle was specified. Path to a file containing PEM data. -
KUBE_CA_PEM(deprecated) - Only if a custom CA bundle was specified. Raw PEM data. -
KUBECONFIG- Path to a file containingkubeconfigfor this deployment. CA bundle would be embedded if specified.
What you can get with the Kubernetes integration
Here's what you can do with GitLab if you enable the Kubernetes integration.
Deploy Boards
Available in GitLab Premium.
GitLab's Deploy Boards offer a consolidated view of the current health and status of each CI environment running on Kubernetes, displaying the status of the pods in the deployment. Developers and other teammates can view the progress and status of a rollout, pod by pod, in the workflow they already use without any need to access Kubernetes.
> Read more about Deploy Boards
Canary Deployments
Available in GitLab Premium.
Leverage Kubernetes' Canary deployments and visualize your canary deployments right inside the Deploy Board, without the need to leave GitLab.
> Read more about Canary Deployments
Kubernetes monitoring
Automatically detect and monitor Kubernetes metrics. Automatic monitoring of NGINX ingress is also supported.
> Read more about Kubernetes monitoring
Auto DevOps
Auto DevOps automatically detects, builds, tests, deploys, and monitors your applications.
To make full use of Auto DevOps(Auto Deploy, Auto Review Apps, and Auto Monitoring) you will need the Kubernetes project integration enabled.
Web terminals
NOTE: Note:
Introduced in GitLab 8.15. You must be the project owner or have master permissions
to use terminals. Support is limited to the first container in the
first pod of your environment.
When enabled, the Kubernetes service adds web terminal
support to your environments. This is based on the exec functionality found in
Docker and Kubernetes, so you get a new shell session within your existing
containers. To use this integration, you should deploy to Kubernetes using
the deployment variables above, ensuring any pods you create are labelled with
app=$CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG. GitLab will do the rest!